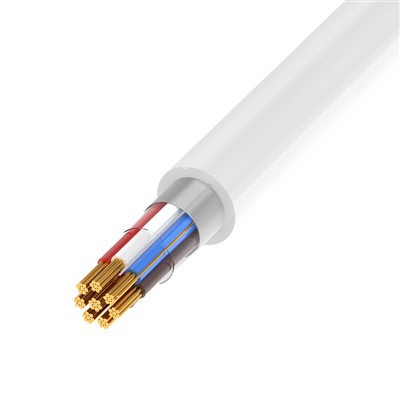
Wire refers to the conductor used to transmit electrical energy. It can be categorized as bare wire, magnet wire, and insulated wire. Bare wire lacks insulation and includes copper and aluminum flat wire, overhead stranded wire, and various profiles (such as profiled wire, busbars, copper and aluminum busbars, etc.). It is primarily used for outdoor overhead wire and indoor busbars and switch boxes.
Magnet wire is an insulated conductor that generates a magnetic field or induces current in a magnetic field when energized. It is primarily used for windings in motors, transformers, and other related electromagnetic equipment. Its conductor, primarily copper, should have a thin insulation layer and excellent electrical and mechanical properties, as well as resistance to heat, moisture, and solvents. Different insulation materials can achieve different properties.
Magnet wire mainly comes in two types: enameled wire and wrapped wire. Enameled wire is made by coating bare copper wire with an insulating varnish. It has a thinner insulation layer and occupies less space, making it widely used in various motors, electrical appliances, and instruments. The performance of enameled wire varies depending on the nature of the insulation material used. Wrapped wire primarily includes yarn-covered wire, silk-covered wire, glass-fiber-covered wire, paper-covered wire, and plastic film-covered wire. Yarn-covered and silk-covered wires are likely to be phased out due to their poor temperature resistance and large size. Glass-fiber-covered wire is made by wrapping glass fibers around round copper wire and impregnating it with silicone resin. It can withstand temperatures up to 180°C and offers excellent insulation and mechanical strength. Paper-covered wire is primarily used in oil-immersed transformers. Plastic film-covered wire is made by coating a polyimide film with an adhesive, wrapping it around a conductor, and then molten-coating it. Its tough and elastic insulation layer is easy to wind, wear-resistant, and heat-resistant, making it widely used in aerospace equipment. Insulated wire generally consists of a conductive core, an insulating layer, and a protective layer.