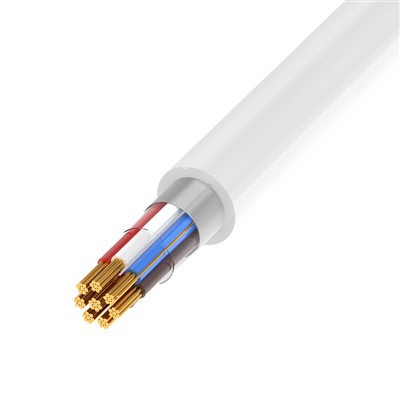
In modern network infrastructure, network cables serve as the physical medium for data transmission, and their performance directly impacts network stability, speed, and reliability. Network cable performance is primarily determined by key factors such as material, structure, transmission rate, and interference resistance.
First, the material of the network cable is crucial to signal transmission quality. Common copper network cables are classified into oxygen-free copper (OFC), copper-clad aluminum (CCA), and all-copper. Due to its high conductivity and low resistance, OFC is the preferred choice for high-performance network cables, suitable for Gigabit and even 10G networks. Copper-clad aluminum, on the other hand, is lower in cost but has poorer conductivity, making it generally only suitable for short-distance, low-speed network environments.
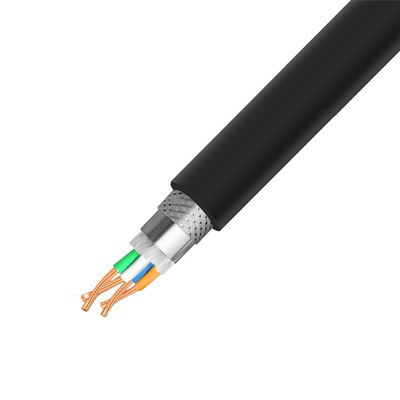
Second, the structure of the network cable determines its interference resistance and transmission mode. Currently, mainstream network cable standards include Category 5e (Category 5e), Category 6 (Category 6), Category 6a (enhanced Category 6), and Category 7 (Category 7). Category 6 and higher network cables utilize a twisted-pair design with an added shielding layer (such as STP or FTP), effectively reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, thereby supporting higher bandwidths (e.g., 10Gbps and higher).
In addition, the transmission rate and maximum transmission distance of a network cable are also important performance indicators. In a standard Ethernet environment, Category 5e supports 1Gbps transmission, while Category 6 can stably support 10Gbps (but limited to a distance of 55 meters). Beyond the standard distance, signal attenuation will cause network performance to degrade, requiring the use of optical fiber or signal amplifiers to compensate.
Finally, interference resistance directly impacts the reliability of a network cable. In strong electromagnetic environments (such as industrial plants or near power facilities), shielded network cables (STP) offer advantages over unshielded cables (UTP), effectively reducing the impact of external interference on data transmission.
In summary, selecting a high-performance network cable requires a comprehensive consideration of material, structure, transmission rate, and interference resistance to ensure efficient and stable network operation.